Which Of The Following Terms Is Used To Describe An Increase In The Size Of Muscle Cells?
Muscle Tissue
Exercise and Muscle Performance
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe hypertrophy and cloudburst
- Explain how resistance exercise builds muscle
- Explain how operation-enhancing substances bear on musculus
Physical training alters the appearance of skeletal muscles and can produce changes in muscle operation. Conversely, a lack of use tin result in decreased performance and muscle appearance. Although muscle cells tin can change in size, new cells are not formed when muscles grow. Instead, structural proteins are added to musculus fibers in a procedure called hypertrophy, then cell diameter increases. The contrary, when structural proteins are lost and muscle mass decreases, is chosen atrophy. Age-related muscle atrophy is called sarcopenia. Cellular components of muscles tin also undergo changes in response to changes in musculus employ.
Endurance Practice
Slow fibers are predominantly used in endurance exercises that require little force only involve numerous repetitions. The aerobic metabolism used by slow-twitch fibers allows them to maintain contractions over long periods. Endurance preparation modifies these ho-hum fibers to brand them even more efficient by producing more mitochondria to enable more aerobic metabolism and more than ATP product. Endurance exercise can also increase the amount of myoglobin in a cell, as increased aerobic respiration increases the need for oxygen. Myoglobin is found in the sarcoplasm and acts as an oxygen storage supply for the mitochondria.
The training can trigger the formation of more than extensive capillary networks effectually the cobweb, a process called angiogenesis, to supply oxygen and remove metabolic waste. To let these capillary networks to supply the deep portions of the muscle, musculus mass does not profoundly increase in lodge to maintain a smaller area for the improvidence of nutrients and gases. All of these cellular changes result in the power to sustain low levels of muscle contractions for greater periods without fatiguing.
The proportion of SO muscle fibers in muscle determines the suitability of that muscle for endurance, and may benefit those participating in endurance activities. Postural muscles have a large number of And so fibers and relatively few FO and FG fibers, to keep the back straight ((Figure)). Endurance athletes, similar marathon-runners also would benefit from a larger proportion of SO fibers, merely it is unclear if the virtually-successful marathoners are those with naturally loftier numbers of SO fibers, or whether the most successful marathon runners develop high numbers of SO fibers with repetitive preparation. Endurance grooming tin can result in overuse injuries such as stress fractures and joint and tendon inflammation.
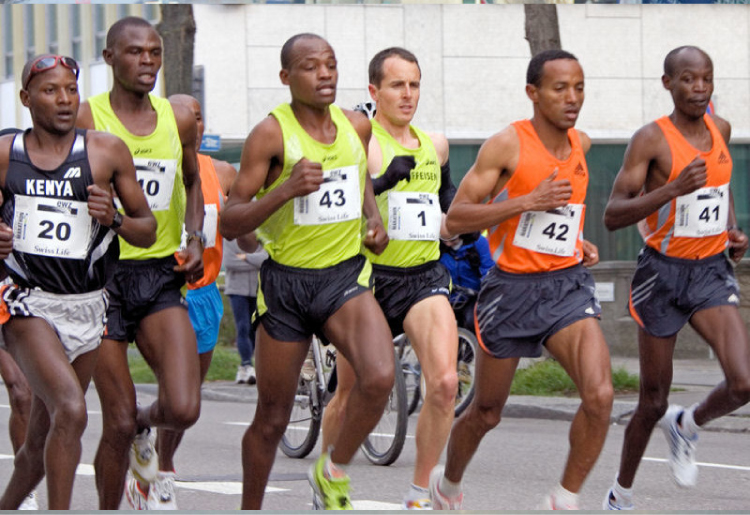
Marathoners
Long-distance runners accept a big number of Then fibers and relatively few FO and FG fibers. (credit: "Tseo2"/Wikimedia Commons)

Resistance Exercise
Resistance exercises, as opposed to endurance practice, require large amounts of FG fibers to produce short, powerful movements that are not repeated over long periods. The high rates of ATP hydrolysis and cantankerous-bridge germination in FG fibers result in powerful muscle contractions. Muscles used for ability accept a higher ratio of FG to SO/FO fibers, and trained athletes possess even higher levels of FG fibers in their muscles. Resistance practise affects muscles past increasing the formation of myofibrils, thereby increasing the thickness of muscle fibers. This added construction causes hypertrophy, or the enlargement of muscles, exemplified past the large skeletal muscles seen in body builders and other athletes ((Figure)). Because this muscular enlargement is achieved past the improver of structural proteins, athletes trying to build muscle mass often ingest large amounts of protein.
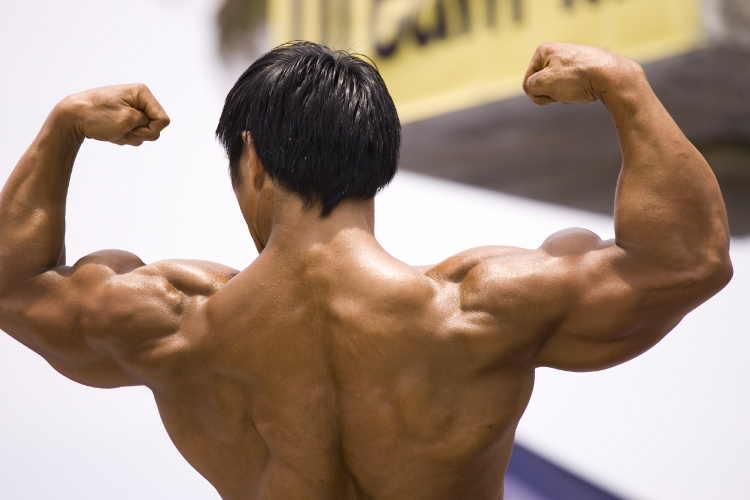
Hypertrophy
Body builders have a large number of FG fibers and relatively few FO and And then fibers. (credit: Lin Mei/flickr)

Except for the hypertrophy that follows an increment in the number of sarcomeres and myofibrils in a skeletal musculus, the cellular changes observed during endurance training do non ordinarily occur with resistance training. There is usually no significant increment in mitochondria or capillary density. Yet, resistance grooming does increase the evolution of connective tissue, which adds to the overall mass of the musculus and helps to incorporate muscles every bit they produce increasingly powerful contractions. Tendons as well get stronger to forbid tendon damage, equally the force produced by muscles is transferred to tendons that adhere the muscle to bone.
For constructive strength training, the intensity of the practice must continually be increased. For instance, continued weight lifting without increasing the weight of the load does not increment muscle size. To produce e'er-greater results, the weights lifted must become increasingly heavier, making information technology more than difficult for muscles to move the load. The muscle then adapts to this heavier load, and an even heavier load must be used if even greater muscle mass is desired.
If done improperly, resistance training tin lead to overuse injuries of the muscle, tendon, or bone. These injuries can occur if the load is likewise heavy or if the muscles are non given sufficient time between workouts to recover or if joints are not aligned properly during the exercises. Cellular damage to musculus fibers that occurs after intense exercise includes damage to the sarcolemma and myofibrils. This musculus damage contributes to the feeling of soreness subsequently strenuous exercise, merely muscles gain mass as this impairment is repaired, and boosted structural proteins are added to replace the damaged ones. Overworking skeletal muscles can also lead to tendon damage and fifty-fifty skeletal damage if the load is too great for the muscles to deport.
Operation-Enhancing Substances
Some athletes attempt to boost their performance by using various agents that may enhance muscle performance. Anabolic steroids are one of the more widely known agents used to boost muscle mass and increase ability output. Anabolic steroids are a form of testosterone, a male person sex activity hormone that stimulates musculus formation, leading to increased muscle mass.
Endurance athletes may as well endeavor to boost the availability of oxygen to muscles to increase aerobic respiration by using substances such equally erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone normally produced in the kidneys, which triggers the production of cherry blood cells. The extra oxygen carried by these blood cells can and then be used by muscles for aerobic respiration. Homo growth hormone (hGH) is some other supplement, and although it can facilitate building musculus mass, its main role is to promote the healing of musculus and other tissues after strenuous exercise. Increased hGH may let for faster recovery later on muscle harm, reducing the remainder required after practice, and allowing for more sustained high-level functioning.
Although performance-enhancing substances often do meliorate performance, most are banned past governing bodies in sports and are illegal for nonmedical purposes. Their use to heighten functioning raises ethical issues of cheating because they give users an unfair advantage over nonusers. A greater concern, however, is that their apply carries serious wellness risks. The side furnishings of these substances are often significant, nonreversible, and in some cases fatal. The physiological strain caused by these substances is oft greater than what the trunk can handle, leading to effects that are unpredictable and unsafe. Anabolic steroid use has been linked to infertility, ambitious behavior, cardiovascular disease, and encephalon cancer.
Similarly, some athletes have used creatine to increase ability output. Creatine phosphate provides quick bursts of ATP to muscles in the initial stages of contraction. Increasing the amount of creatine available to cells is thought to produce more ATP and therefore increase explosive power output, although its effectiveness as a supplement has been questioned.
Everyday Connection
Aging and Muscle Tissue Although cloudburst due to decay can often be reversed with exercise, musculus atrophy with age, referred to as sarcopenia, is irreversible. This is a chief reason why even highly trained athletes succumb to declining operation with historic period. This decline is noticeable in athletes whose sports require forcefulness and powerful movements, such as sprinting, whereas the effects of age are less noticeable in endurance athletes such as marathon runners or long-distance cyclists. As muscles age, musculus fibers die, and they are replaced by connective tissue and adipose tissue ((Effigy)). Considering those tissues cannot contract and generate forcefulness as musculus can, muscles lose the ability to produce powerful contractions. The decline in muscle mass causes a loss of strength, including the forcefulness required for posture and mobility. This may exist caused past a reduction in FG fibers that hydrolyze ATP quickly to produce brusk, powerful contractions. Muscles in older people sometimes possess greater numbers of Then fibers, which are responsible for longer contractions and do not produce powerful movements. There may also be a reduction in the size of motor units, resulting in fewer fibers being stimulated and less muscle tension existence produced.
Atrophy
Muscle mass is reduced as muscles atrophy with decay.
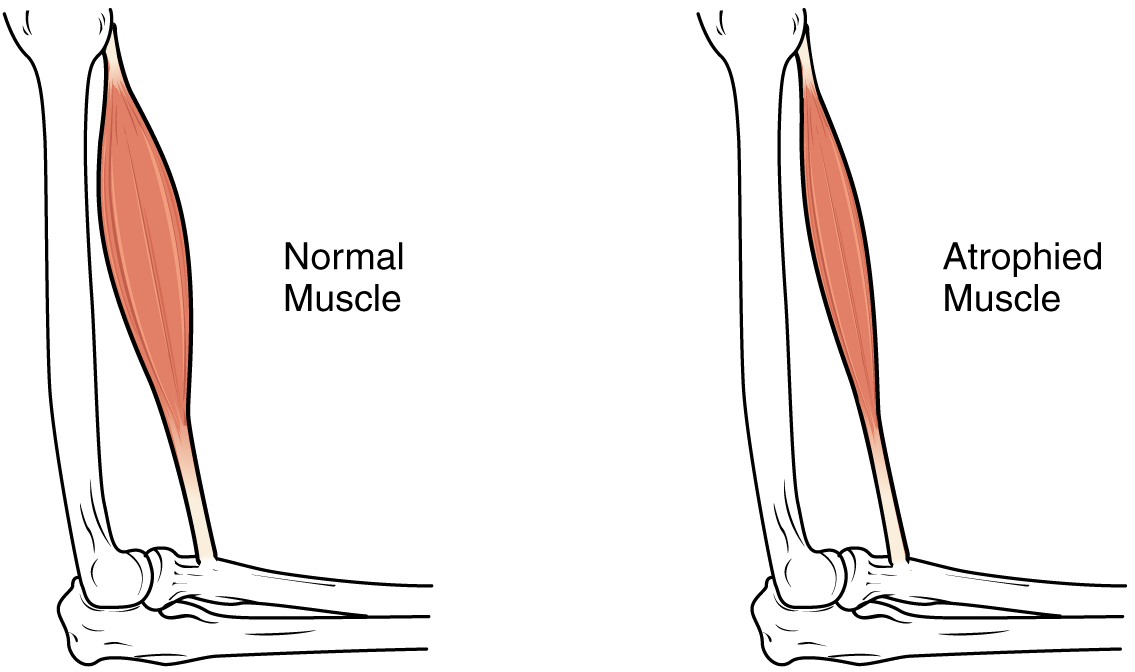
Sarcopenia can be delayed to some extent by exercise, as training adds structural proteins and causes cellular changes that can offset the effects of cloudburst. Increased practise tin produce greater numbers of cellular mitochondria, increase capillary density, and increase the mass and strength of connective tissue. The effects of historic period-related atrophy are especially pronounced in people who are sedentary, equally the loss of musculus cells is displayed as functional impairments such equally trouble with locomotion, residue, and posture. This tin can pb to a decrease in quality of life and medical issues, such as joint problems considering the muscles that stabilize basic and joints are weakened. Problems with locomotion and balance can too cause various injuries due to falls.
Chapter Review
Hypertrophy is an increment in muscle mass due to the addition of structural proteins. The reverse of hypertrophy is atrophy, the loss of muscle mass due to the breakdown of structural proteins. Endurance exercise causes an increase in cellular mitochondria, myoglobin, and capillary networks in So fibers. Endurance athletes have a high level of And so fibers relative to the other fiber types. Resistance exercise causes hypertrophy. Power-producing muscles have a higher number of FG fibers than of slow fibers. Strenuous exercise causes muscle cell harm that requires time to heal. Some athletes use performance-enhancing substances to enhance musculus performance. Muscle atrophy due to age is called sarcopenia and occurs equally muscle fibers die and are replaced by connective and adipose tissue.
Review Questions
The muscles of a professional person sprinter are virtually likely to have ________.
- fourscore percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and 20 pct slow-twitch muscle fibers
- 20 percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and 80 percentage slow-twitch muscle fibers
- l per centum fast-twitch muscle fibers and 50 percentage slow-twitch muscle fibers
- twoscore percentage fast-twitch muscle fibers and 60 percent slow-twitch musculus fibers
The muscles of a professional marathon runner are most probable to have ________.
- 80 percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and 20 percent wearisome-twitch muscle fibers
- 20 pct fast-twitch musculus fibers and 80 percent slow-twitch musculus fibers
- 50 percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and fifty percent tedious-twitch muscle fibers
- 40 pct fast-twitch muscle fibers and sixty per centum wearisome-twitch musculus fibers
Which of the following statements is true?
- Fast fibers have a pocket-size diameter.
- Fast fibers comprise loosely packed myofibrils.
- Fast fibers have big glycogen reserves.
- Fast fibers have many mitochondria.
Which of the following statements is false?
- Tiresome fibers take a modest network of capillaries.
- Dull fibers contain the pigment myoglobin.
- Slow fibers contain a large number of mitochondria.
- Dull fibers contract for extended periods.
Critical Thinking Questions
What changes occur at the cellular level in response to endurance training?
Endurance training modifies slow fibers to make them more efficient by producing more mitochondria to enable more aerobic metabolism and more ATP product. Endurance practice can too increase the amount of myoglobin in a cell and formation of more all-encompassing capillary networks around the fiber.
What changes occur at the cellular level in response to resistance training?
Resistance exercises affect muscles past causing the formation of more than actin and myosin, increasing the construction of muscle fibers.
Glossary
- angiogenesis
- formation of blood capillary networks
- atrophy
- loss of structural proteins from musculus fibers
- hypertrophy
- improver of structural proteins to musculus fibers
- sarcopenia
- age-related musculus atrophy
Which Of The Following Terms Is Used To Describe An Increase In The Size Of Muscle Cells?,
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiologyopenstax/chapter/exercise-and-muscle-performance/
Posted by: savoiesendes.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Terms Is Used To Describe An Increase In The Size Of Muscle Cells?"
Post a Comment